
Pay-Per-Click
PPC, or Pay-Per-Click, is an online advertising model where advertisers pay a fee each time their ad is clicked by a user. It is commonly used to drive traffic to websites and generate leads or sales quickly. PPC ads are typically shown on search engines (like Google), social media platforms, or display networks. Advertisers bid on specific keywords relevant to their target audience, and their ads appear when users search for those terms. The ad position and cost depend on factors like bid amount, ad quality, and relevance. PPC provides measurable results, allowing businesses to track performance and optimize campaigns for better returns.
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) is a powerful digital advertising model that allows businesses to drive targeted traffic to their websites by paying only when users click on their ads. Unlike traditional advertising, where you pay a flat fee for visibility, PPC ensures you’re only charged when someone actively engages with your ad, making it a cost-effective way to reach potential customers
How PPC Work
At the heart of PPC is a bidding system. Advertisers bid on specific keywords that are relevant to their business. For example, if you run a clothing store, you might bid on keywords like “buy men’s jackets” or “best women’s shoes.” When users search for these terms, your ad appears at the top of search results (on platforms like Google), or within social media feeds, or as banner ads on websites. Each time someone clicks on your ad, you pay a predetermined fee, which depends on the competition for that keyword and the quality of your ad.
PPC (Pay-Per-Click) works by allowing advertisers to bid on specific keywords relevant to their business. When a user searches for one of these keywords, ads appear at the top of search engine results or on websites. Advertisers are charged each time someone clicks on their ad.
Here’s how it works step-by-step:
- Bidding: Advertisers set bids on keywords they want to target.
- Ad Auction: When a user searches for that keyword, an auction determines which ads will appear, based on both the bid and the quality of the ad (e.g., relevance and user experience).
- Ad Display: The winning ad is displayed, and the advertiser pays when a user clicks on it.
- Tracking & Optimization: Advertisers monitor clicks, conversions, and return on investment (ROI), making adjustments to improve performance.
Work Process of PPC
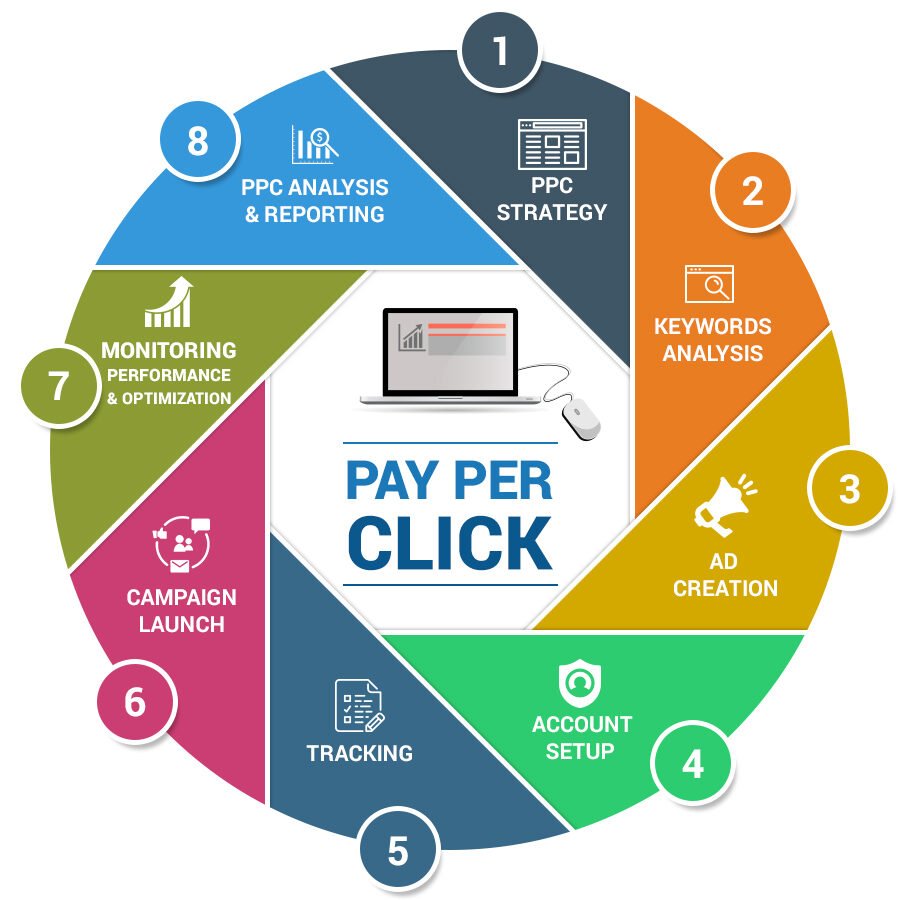
Types of PPC Ads-
1.Search Ads
- Description: These are text-based ads displayed on search engine results pages (SERPs) when users type in specific keywords. Search ads are triggered by queries relevant to the advertiser’s product or service.
- How They Work: Advertisers bid on specific keywords. When a user searches for those terms, ads appear at the top or bottom of the search results. The advertiser pays when the ad is clicked.
- Benefits:
- Directly targets users who are actively searching for specific products or services.
- High-intent traffic, meaning potential customers are closer to making a purchase decision.
- Can be highly customized with extensions (call, location, sitelinks, etc.).
- Platforms: Google Ads, Bing Ads.
- Best For: Businesses wanting to attract users looking for specific products or services, such as e-commerce, local services, or professional services.
2.Display Ads
- Description: Display ads are image-based or rich media ads that appear on websites across the internet, within the Google Display Network (GDN) or other ad networks. These ads are shown to users while they browse different sites, not only on search results.
- How They Work: Display ads are targeted based on user behavior, interests, demographics, and content on specific websites. Advertisers can also retarget users who have previously visited their website.
- Benefits:
- Great for building brand awareness and visibility.
- Typically less expensive per click than search ads.
- Effective for retargeting users who have shown interest in your brand.
- Platforms: Google Display Network, AdRoll, Criteo.
- Best For: Businesses focused on brand awareness, lead nurturing, and reaching a large, broad audience.
3.Shopping Ads
- Description: Shopping ads are product-based ads that show an image, price, store name, and sometimes reviews. These ads appear on search engines like Google or Bing when users search for specific products.
- How They Work: Advertisers create product listings through their Merchant Center (Google) or Microsoft Shopping Campaigns. When users search for related products, these ads appear at the top of the search results. Advertisers pay when users click on the ad and visit the product page.
- Benefits:
- Visually engaging and displays relevant product details upfront.
- Great for e-commerce businesses to promote individual products.
- Highly targeted to users looking for specific products, resulting in higher conversion rates.
- Platforms: Google Shopping, Microsoft Shopping.
- Best For: E-commerce stores looking to promote products directly in search results.
4.Video Ads
- Description: Video ads are advertisements that appear before, during, or after video content, often on platforms like YouTube or within social media feeds.
- How They Work: Advertisers create video content that’s shown to viewers either before their chosen video content (pre-roll), during it (mid-roll), or afterward (post-roll). They can also appear in YouTube search results or in-stream. Video ads can be skippable or non-skippable.
- Benefits:
- Great for storytelling, brand awareness, and engagement.
- Highly engaging as video content captures user attention better than text or image ads.
- Can be targeted based on user interests, demographics, and viewing history.
- Platforms: YouTube Ads, Facebook Video Ads, Instagram, TikTok, Snapchat.
- Best For: Businesses that want to showcase products through engaging visual content, build brand awareness, or tell a brand story.
5.Social Media Ads
- Description: Social media ads are PPC ads that appear within social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Twitter, and others. They can take various forms, such as text, image, video, or carousel (multiple images in a single ad).
- How They Work: Advertisers create campaigns targeting specific demographics (age, gender, location), interests, behaviors, or custom audiences (based on previous interactions, like website visits). These ads appear in users’ feeds or sidebars.
- Benefits:
- Granular targeting based on user behavior, demographics, and interests.
- Engages users on platforms they frequently use, increasing visibility and brand interaction.
- Various ad formats allow for creative flexibility.
- Platforms: Facebook Ads, Instagram Ads, LinkedIn Ads, Twitter Ads, TikTok Ads.
- Best For: Businesses looking to target specific audience segments based on interests and demographics, especially for brand awareness, lead generation, or product promotion.
6.Remarketing Ads
- Description: Remarketing (or retargeting) ads are shown to users who have previously interacted with a business’s website, app, or content but didn’t convert (make a purchase or complete a goal).
- How They Work: By placing a tracking pixel on the website, advertisers can serve ads to users who have visited their site or completed specific actions (like adding a product to a cart but not purchasing). These ads are displayed to users as they browse other websites or social media platforms.
- Benefits:
- Helps re-engage potential customers who showed interest but didn’t convert.
- Boosts conversion rates by keeping the brand top-of-mind.
- Often more cost-effective since it targets warm leads.
- Platforms: Google Ads (Remarketing), Facebook Remarketing, AdRoll, Criteo.
- Best For: Businesses that want to convert warm leads into paying customers, especially e-commerce or service-based businesses.

Benefits of PPC Advertising
PPC (Pay-Per-Click) advertising is a digital marketing model where advertisers pay a fee each time their ad is clicked. It’s a way to buy traffic to a website rather than earning it organically. PPC ads can appear on search engines, social media platforms, and other websites, and they are highly targeted to specific audiences based on keywords, demographics, or interests.
Here are the key benefits of PPC advertising:
Immediate Results: PPC provides quick visibility, delivering traffic as soon as ads go live.
Highly Targeted: You can target specific demographics, locations, devices, interests, and keywords, ensuring your ads reach the right audience.
Measurable and Trackable: PPC platforms offer detailed analytics on ad performance, allowing businesses to measure ROI and make data-driven decisions.
Cost Control: You set your own budget and only pay when someone clicks on your ad, giving you control over costs.
Brand Exposure: PPC increases visibility, helping to build brand awareness even if users don’t click on the ad.
Retargeting Opportunities: PPC allows you to retarget users who’ve interacted with your site but haven’t converted.
Increases Conversions: With the right optimization, PPC drives high-intent traffic, increasing conversions and sales.
Flexibility: Campaigns can be easily adjusted to respond to changing market conditions or new business goals.
Competitive Advantage: PPC can help smaller businesses compete with larger brands by getting ads in front of potential customers at the top of search results.
Granular Targeting Options: You can refine your targeting with options like age, location, language, and even time of day, ensuring that ads are shown to the most relevant audiences.
Customization with Ad Extensions: PPC platforms like Google Ads offer extensions that allow businesses to include more information (e.g., phone numbers, site links), enhancing ad effectiveness.
Works Well with SEO: PPC provides immediate traffic while you build your organic SEO rankings, creating a powerful combination for long-term success.
Local and Global Reach: You can tailor campaigns to target local customers or expand your reach globally, depending on your business needs.
Control over Ad Schedule: With PPC, you can choose when your ads run, ensuring they appear when your target audience is most likely to be online.
Improves Brand Recall: Even if users don’t click on your ad, repeated exposure can help improve brand recall, making users more likely to consider your brand later.
Keyword Research & Bidding Strategies
Keyword research involves identifying the terms and phrases your target audience is searching for, and using them in your PPC campaigns to attract relevant traffic.
-
Tools for Keyword Research:
- Google Keyword Planner: Helps find relevant keywords and provides data on search volume, competition, and bid estimates.
- SEMrush : Offers competitor keyword analysis, search volumes, and keyword difficulty scores.
- Uber suggest: Generates keyword ideas and insights on performance metrics.
- Answer The Public: Provides long-tail keyword ideas based on user questions and search intent.
-
Types of Keywords:
-
- Short-Tail Keywords: Broad, one- or two-word phrases (e.g., “shoes”). High search volume but very competitive.
- Long-Tail Keywords: Longer, more specific phrases (e.g., “women’s running shoes size 9”). Lower search volume but more targeted, often leading to higher conversion rates.
- Branded Keywords: Keywords related to your brand name.
- Competitor Keywords: Keywords associated with competitors, used to target their customers.
-
Keyword Match Types:
- Broad Match: Shows ads for any search that includes the keyword or related variations, maximizing reach.
- Phrase Match: Ads appear for searches that include the exact phrase or a close variation.
- Exact Match: Ads are triggered by searches matching the keyword exactly, offering the highest control and relevance.
- Negative Keywords: Excludes certain terms to prevent ads from appearing for irrelevant searches.
-
Intent-based Keywords:
- Transactional Keywords: Used by people ready to make a purchase (e.g., “buy shoes online”).
- Informational Keywords: Used by people seeking information (e.g., “how to clean leather shoes”).
- Commercial Keywords: Indicating a user may soon make a purchase (e.g., “best running shoes 2024”).
Bidding Strategies for PPC
Once you have the right keywords, the next step is to set a bidding strategy that fits your goals and budget. Here are common bidding strategies:
Manual Bidding:
- Description: You set maximum bids for keywords manually.
- Best For: Tight control over budget and cost-per-click (CPC), suitable for experienced advertisers who want granular control.
- Pros: Full control over how much you’re willing to pay for each click.
- Cons: Time-consuming as it requires constant monitoring and adjustments.
Automated Bidding:
- Description: The ad platform (e.g., Google Ads) adjusts bids automatically based on performance data to achieve specific campaign goals.
- Types of Automated Bidding:
- Maximize Clicks: Focuses on getting as many clicks as possible within your budget.
- Target CPA (Cost Per Acquisition): Optimizes bids to achieve a specific cost per conversion.
- Target ROAS (Return on Ad Spend): Bids are adjusted to maximize revenue based on a target ROAS.
- Enhanced CPC (ECPC): Combines manual bidding with automated bid adjustments to improve conversion likelihood.
- Maximize Conversions: Automatically sets bids to get the highest number of conversions within your budget.
- Best For: Advertisers who want to save time and leverage machine learning for bid optimization.
Bid Adjustments:
- Device-Based Bidding: You can adjust bids based on whether users are on mobile, desktop, or tablets.
- Location-Based Bidding: Adjust bids depending on where the user is located (local or international).
- Time-Based Bidding: Increase or decrease bids based on the time of day or day of the week when your ads perform best.
- Audience-Based Bidding: Adjust bids based on user behavior, demographics, or interests.
Bid Budgeting:
- Daily Budget: You set a daily limit for how much you want to spend on a campaign.
- Shared Budgets: Allocate a single budget across multiple campaigns, allowing more flexibility.
Competitor Bidding:
- Description: Bidding on competitor keywords (e.g., targeting users searching for a competitor’s brand).
- Risks: It can be costly and may lead to irrelevant clicks, so monitor closely.
Bid Cap:
- Description: Setting a maximum cost-per-click (CPC) to prevent overspending on high-cost keywords.
- Use Case: To maintain control over costs, especially for keywords with fluctuating CPC rates.
First-Position Bidding:
- Description: Aiming to outbid competitors for the top ad position.
- Risks: It can lead to overspending, so balance your bid amount with the potential ROI.
